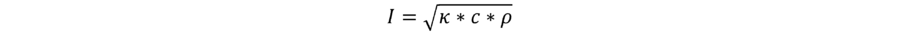What is KRC
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| − | :These three variables are used in the equation for | + | :These three variables are used in the equation for thermal inertia: |
[[Image:Thermal_Inertia.png|900px]] | [[Image:Thermal_Inertia.png|900px]] | ||
Revision as of 18:48, 24 July 2018
Description
- KRC is incredibly flexible and has a wide range of functionality. Therefore, it is important to learn the basic capability of KRC.
- What can it do?
- How does it work?
- What conditions can be adjusted within the model?
- In short, KRC can do a great deal and can vary almost any condition desired. The KRC Davinci Interface is a sufficient and comprehensive method for using KRC. Therefore, the KRC Davinci Interface is the recommended method to use KRC.
KRC is a numerical thermal model used to determine the surface temperature of bodies in the Solar System. A numerical model takes input parameters to generate a virtual environment based on the conditions specified by the user. Once the environment is established, the model is able to extrapolate the most plausible values for certain variables that were excluded from the initial conditions. KRC, in particular, is a thermal model, therefore it deals with temperature and related quantities. Every variable KRC uses in its calculations can be an input parameter from the user. For example, if I know the latitude, longitude, albedo, opacity, and elevation of a location the KRC model will be able to tell extrapolate the surface temperature. This allows users extensive control over the model, generating a wide range of conditions to suit any desired environment.
- KRC:
- K stands for κ (kappa), the variable for conductivity
- R stands for ρ (rho), the variable for density
- C stands for cp, the variable for specific heat
- These three variables are used in the equation for thermal inertia:
- For a deeper understanding of thermodynamics and how it is used in remote sensing and physics, please visit the Thermodynamics Wikipedia page
- For thorough understanding of KRC:
- Suggested Reading:
- Kieffer 2013 (Online Article) or Download PDF
- Power Point from 2013 KRC Conference.
- Suggested Video: