Planetary Fluxes
(→Noticeable Diurnal Temperatures Cycle (Mars, Pluto, etc.)) |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
The simplest approach consist in using default builtin values from the KRC support files: | The simplest approach consist in using default builtin values from the KRC support files: | ||
| − | OUT = krc(lat = 0., INERTIA = 70., body = " | + | OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=0.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") |
But any input value can be forced: | But any input value can be forced: | ||
| − | ::BT_Avg : Average Brightness Temperature [K] | + | ::'''BT_Avg''' : Average Brightness Temperature [K] |
| − | ::BT_Min : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K] | + | ::'''BT_Min''' : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K] |
| − | ::BT_Max : Max Brightness Temperature [K] | + | ::'''BT_Max''' : Max Brightness Temperature [K] |
| − | ::Dis_AU : Distance from Sun in AU | + | ::'''Dis_AU''' : Distance from Sun in AU |
| − | ::Geom_alb : Geometric Albedo [1] | + | ::'''Geom_alb''' : Geometric Albedo [1] |
| − | ::Mut_Period : Mutual Period [?] | + | ::'''Mut_Period''' : Mutual Period [?] |
| − | ::Orb_Radius : Orbiting Radius [km] | + | ::'''Orb_Radius''' : Orbiting Radius [km] |
| − | ::Radius : Radius of the Orbiting body [km] | + | ::'''Radius''' : Radius of the Orbiting body [km] |
| − | ::Lon_Hr : | + | ::'''Lon_Hr''' : Surface longitude relative to the sub-planet point, expressed in hours. Lon_Hr = 12. is the sub-main planet point (max fluxes), and 0. for the center longitude of the satellite hidden face. Note 18 < Lon_Hr%24 < 6 corresponds to the body's hidden face, so no fluxes are contributed in these cases. |
| − | + | Generally, for tidally locked bodies, the sub-planet point is located ~ at longitude = 0, so that Lon_Hr can be derived from the local longitude: Lon_Hr = (24/360 x (180 - longitude west))%24 | |
| + | OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=0.55,PFlux="T",BT_Avg=127.,BT_Min=127.,BT_Max=127.,Dis_AU=5.203,Geom_alb=0.52,Mut_Period=3.55,Orb_Radius=670900,Radius=670900,Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Europa_F02.png|800px]] | ||
===Noticeable Diurnal Temperatures Cycle (Mars, Pluto, etc.)=== | ===Noticeable Diurnal Temperatures Cycle (Mars, Pluto, etc.)=== | ||
| − | This case applies to satellites revolving around planets experienced pronounced diurnal cycles like Phobos around Mars. The IR flux is not only a function of the solid angle of the emitting body, but also a function of the local time of the emitting body. | + | This case applies to satellites revolving around planets experienced pronounced diurnal cycles like Phobos around Mars. The IR flux is not only a function of the solid angle of the emitting body, but also a function of the local time of the emitting body. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | :: 1: The user provides IR and Vis tables, for example a realistic case from this file ([[File:67.1_AvgFluxes.txt]]), or made up data for this example: | ||
| − | + | LTST = create(1,12,1,start=0.5,step=2,format=float) | |
| + | IR_Table = translate(00.0//00.0//01.0//03.8//08.5//12.0//13.0//11.5//08.0//03.5//01.0//00.0,from=x,to=y) | ||
| + | Vis_Table = translate(09.0//08.0//08.0//10.0//15.0//23.0//28.0//30.0//24.0//17.0//12.0//10.0,from=x,to=y) | ||
| − | + | :: 2: Make IR an array with IR flux x LTST x 1 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | :: 3: Make Vis an array with Vis flux x LTST x 1 | |
| + | Then the user can invoke the fluxes with PFlux = "T", Lon_Hr = Lon_Hr, IR = IR, Vis = Vis | ||
| + | The IR and visible fluxes are modeled by fitting a sin wave through the max and min radiance values, and KRC accepts parameters describing these two sin functions (IR, and VIS). | ||
| + | The example below emulates the interface's fit to the fluxes provided by the user: | ||
| + | Vis_1 = cat(Vis_Table,LTST,axis=x) | ||
| + | IR_1 = cat(IR_Table,LTST,axis=x) | ||
| + | IR = IR_1[1,,1] | ||
| + | LTST_IR = IR_1[2,,1] | ||
| + | Vis = Vis_1[1,,1] | ||
| + | LTST_Vis = Vis_1[2,,1] | ||
| + | Peak_IR = maxpos(IR,showval=1) | ||
| + | Min_IR = minpos(IR,showval=1) | ||
| + | LTST_IR_Peak = LTST_IR[1,int(Peak_IR[2,1,1]),1] | ||
| + | Half_Amp_IR = 0.5*(Peak_IR[4]-Min_IR[4]) | ||
| + | Phase_IR = 360.*LTST_IR_Peak/24. | ||
| + | IR_KRC = (Min_IR[4] + Half_Amp_IR * (1 + cosd(360.*LTST_IR/24. - Phase_IR))) | ||
| + | Peak_Vis = maxpos(Vis,showval=1) | ||
| + | Min_Vis = minpos(Vis,showval=1) | ||
| + | LTST_Vis_Peak = LTST_Vis[1,int(Peak_Vis[2,1,1]),1] | ||
| + | Half_Amp_Vis = 0.5*(Peak_Vis[4]-Min_Vis[4]) | ||
| + | Phase_Vis = 360.*LTST_Vis_Peak/24. | ||
| + | Vis_KRC = (Min_Vis[4] + Half_Amp_Vis * (1 + cosd(360.*LTST_Vis/24. - Phase_Vis))) | ||
| + | plot(Vis_Table,"User-provided Vis from Mars",IR_Table,"User-provided IR from Mars",Vis_KRC,"KRC-derived Vis from Mars",IR_KRC,"KRC-derived IR from Mars",(Vis_Table+IR_Table)-(IR_KRC+Vis_KRC),"User-provided vs KRC_provided",w=4,Xaxis=LTST) | ||
| + | [[Image:Phobos_Fluxes_2.png|800px]] External IR and visible fluxes, their best sin fits as fed to KRC by the interface, and the resulting flux error. | ||
| + | out = krc(INERTIA=35.,lat=10.,body="Phobos",ls=Ls,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=Lon_Hr,IR=IR_1,Vis=Vis_1) | ||
| + | Davinci function krc_planetary_flux_table(IR,Vis,Lon_Hr) | ||
| + | DaVinci function krc_planetary_flux_porb(porb,porb_Planet,Lon_Hr) | ||
| + | [[File:Flux_Forcing_01112018.xlsx]] | ||
| + | Generally, Phobos modeling requires the addition of the visible and IR fluxes from Mars: | ||
| + | out = krc(lat = 12. ,INERTIA = 50. ,body = "Phobos", LKofT = "T", PFlux = "T", Lon_Hr = 8.) | ||
| + | ...if standard flux values are acceptable (i.e., broad assumption on Mars surface temperature, and albedo). Fluxes are set with PFlux = "T", and by setting Lon_Hr. | ||
| + | Lon_Hr is the surface longitude relative to the sub-Mars point, expressed in hours. Phobos being tidally locked, Lon_Hr = 12. is the sub-Mars point (max fluxes), and 0. for the center longitude of Phobos hidden face. Note 18 < Lon_Hr%24 < 6 corresponds to the Phobos hidden face, so no fluxes are contributed in these cases. | ||
| − | + | Generally, for tidally locked bodies, the sub-planet point (sub Mars point for Phobos is located ~ at longitude = 0), so that Lon_Hr can be derived from the longitude modeled on Phobos ore any tidally locked body: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Lon_Hr = (24/360 x (180 - longitude west))%24 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Phobos_Fluxes_1.png|800px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Alternatively, the user can provide Visible and IR fluxes versus local time (krc_planetary_flux_table() generates the input parameters). An external model or a set of dedicated KRC runs can be used to determine the IR and Visible flux versus local time, as seen from Lon_Hr and the specified latitude. The figure below shows the externally provided values ("IR External Model", and "Vis External Model", the associated sin fits fed to KRC by the interface ("IR KRC Fit", and "Vis KRC Fit"), and the difference between the external forcing and the KRC forcing ("KRC - External Model"). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Note that a user might want to consider reducing the average difference between the KRC Fit and the external model by fine tuning the fits. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | In this case, the flux from Mars on Phobos can be formalized like this: | ||
| + | out = krc(lat = 12. ,INERTIA = 50. ,body = "Phobos", LKofT = "T", PFlux = "T",Lon_Hr = 8., IR = IR_1, Vis = Vis_1) | ||
| − | + | See below a comparison of the predicted surface temperature with and without Mars IR and visible shine on Phobos: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Phobos_Fluxes_Diff.png|800px]] Comparison between No Flux, and Flux at the Sub Mars point | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Lon_Hr_Phobos.png|800px]] Comparison between No Flux, and Flux received from the hidden face (none), i.e., no forcing. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 20:12, 1 June 2020
Incoming visible and IR fluxes contributed by nearby bodies can be specified, for example Mars shine on Phobos, or Jupiter shine on Europa. Set:
PFlux = "T" Lon_Hr = [0-24]
in KRC, fluxes take the form of sin functions characterized by various nonintuitive parameters (see helplist).
The DaVinci interface generates these parameters and feed them to KRC from default parameters or user-defined values. In both cases, various assumptions and fits are performed.
While the incoming visible flux is generally straightforward to calculate, the incoming IR flux can be more complex to determine for bodies with strong diurnal temperature variations (like Mars, unlike Jupiter for example).
[edit] Fixed Diurnal Temperatures (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, etc.)
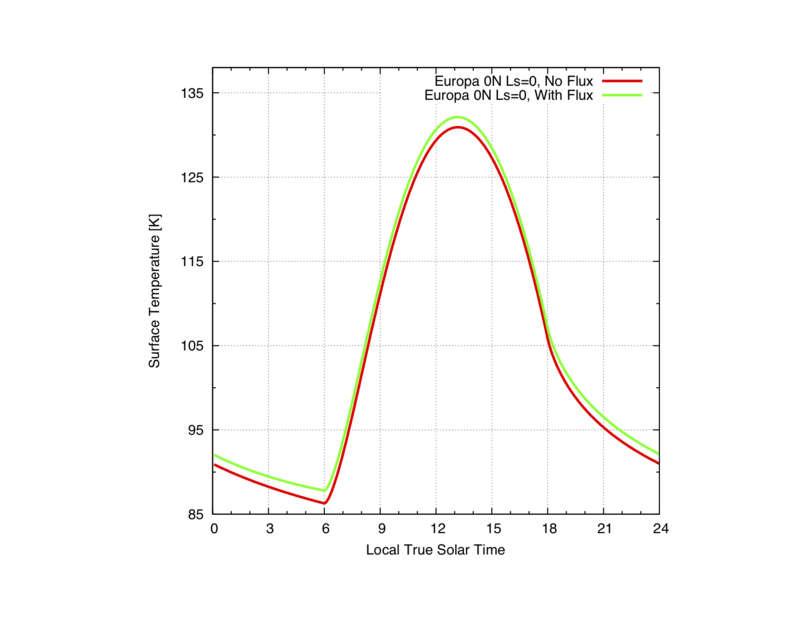
This case applies to satellites revolving around gas giants, or low diurnal contrast bodies (Venus, if it had satellites) etc. The IR flux is only a function of the solid angle of the emitting body. The visible flux follows a sin function over the course of a day. Fewest assumptions used.
The simplest approach consist in using default builtin values from the KRC support files:
OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=0.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
But any input value can be forced:
- BT_Avg : Average Brightness Temperature [K]
- BT_Min : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K]
- BT_Max : Max Brightness Temperature [K]
- Dis_AU : Distance from Sun in AU
- Geom_alb : Geometric Albedo [1]
- Mut_Period : Mutual Period [?]
- Orb_Radius : Orbiting Radius [km]
- Radius : Radius of the Orbiting body [km]
- Lon_Hr : Surface longitude relative to the sub-planet point, expressed in hours. Lon_Hr = 12. is the sub-main planet point (max fluxes), and 0. for the center longitude of the satellite hidden face. Note 18 < Lon_Hr%24 < 6 corresponds to the body's hidden face, so no fluxes are contributed in these cases.
Generally, for tidally locked bodies, the sub-planet point is located ~ at longitude = 0, so that Lon_Hr can be derived from the local longitude: Lon_Hr = (24/360 x (180 - longitude west))%24
OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=0.55,PFlux="T",BT_Avg=127.,BT_Min=127.,BT_Max=127.,Dis_AU=5.203,Geom_alb=0.52,Mut_Period=3.55,Orb_Radius=670900,Radius=670900,Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
[edit] Noticeable Diurnal Temperatures Cycle (Mars, Pluto, etc.)
This case applies to satellites revolving around planets experienced pronounced diurnal cycles like Phobos around Mars. The IR flux is not only a function of the solid angle of the emitting body, but also a function of the local time of the emitting body.
- 1: The user provides IR and Vis tables, for example a realistic case from this file (File:67.1 AvgFluxes.txt), or made up data for this example:
LTST = create(1,12,1,start=0.5,step=2,format=float) IR_Table = translate(00.0//00.0//01.0//03.8//08.5//12.0//13.0//11.5//08.0//03.5//01.0//00.0,from=x,to=y) Vis_Table = translate(09.0//08.0//08.0//10.0//15.0//23.0//28.0//30.0//24.0//17.0//12.0//10.0,from=x,to=y)
- 2: Make IR an array with IR flux x LTST x 1
- 3: Make Vis an array with Vis flux x LTST x 1
Then the user can invoke the fluxes with PFlux = "T", Lon_Hr = Lon_Hr, IR = IR, Vis = Vis
The IR and visible fluxes are modeled by fitting a sin wave through the max and min radiance values, and KRC accepts parameters describing these two sin functions (IR, and VIS). The example below emulates the interface's fit to the fluxes provided by the user:
Vis_1 = cat(Vis_Table,LTST,axis=x) IR_1 = cat(IR_Table,LTST,axis=x) IR = IR_1[1,,1] LTST_IR = IR_1[2,,1] Vis = Vis_1[1,,1] LTST_Vis = Vis_1[2,,1] Peak_IR = maxpos(IR,showval=1) Min_IR = minpos(IR,showval=1) LTST_IR_Peak = LTST_IR[1,int(Peak_IR[2,1,1]),1] Half_Amp_IR = 0.5*(Peak_IR[4]-Min_IR[4]) Phase_IR = 360.*LTST_IR_Peak/24. IR_KRC = (Min_IR[4] + Half_Amp_IR * (1 + cosd(360.*LTST_IR/24. - Phase_IR))) Peak_Vis = maxpos(Vis,showval=1) Min_Vis = minpos(Vis,showval=1) LTST_Vis_Peak = LTST_Vis[1,int(Peak_Vis[2,1,1]),1] Half_Amp_Vis = 0.5*(Peak_Vis[4]-Min_Vis[4]) Phase_Vis = 360.*LTST_Vis_Peak/24. Vis_KRC = (Min_Vis[4] + Half_Amp_Vis * (1 + cosd(360.*LTST_Vis/24. - Phase_Vis)))
plot(Vis_Table,"User-provided Vis from Mars",IR_Table,"User-provided IR from Mars",Vis_KRC,"KRC-derived Vis from Mars",IR_KRC,"KRC-derived IR from Mars",(Vis_Table+IR_Table)-(IR_KRC+Vis_KRC),"User-provided vs KRC_provided",w=4,Xaxis=LTST)
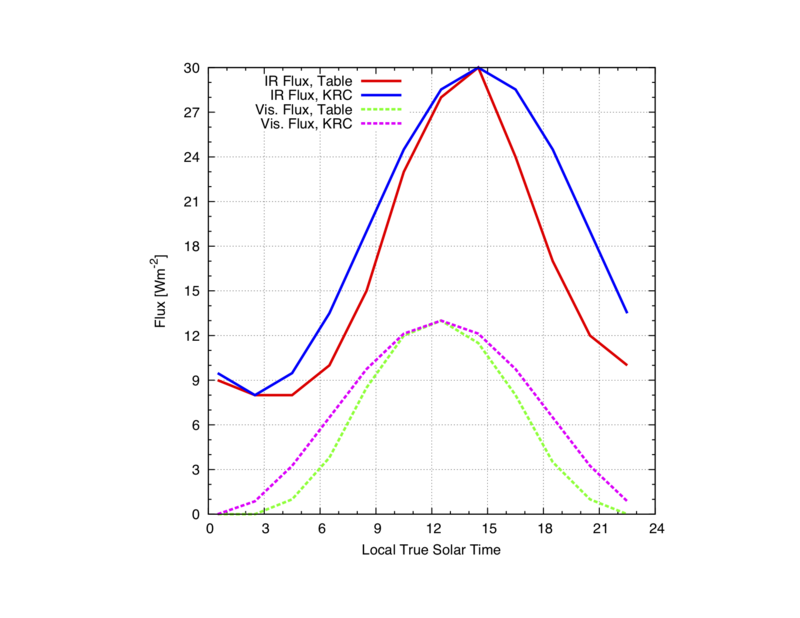 External IR and visible fluxes, their best sin fits as fed to KRC by the interface, and the resulting flux error.
External IR and visible fluxes, their best sin fits as fed to KRC by the interface, and the resulting flux error.
out = krc(INERTIA=35.,lat=10.,body="Phobos",ls=Ls,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=Lon_Hr,IR=IR_1,Vis=Vis_1)
Davinci function krc_planetary_flux_table(IR,Vis,Lon_Hr) DaVinci function krc_planetary_flux_porb(porb,porb_Planet,Lon_Hr)
File:Flux Forcing 01112018.xlsx
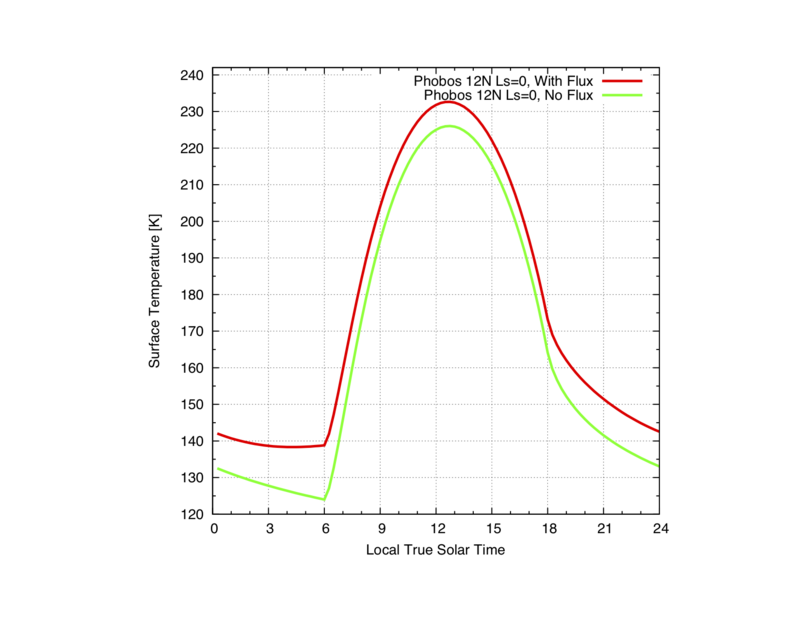
Generally, Phobos modeling requires the addition of the visible and IR fluxes from Mars:
out = krc(lat = 12. ,INERTIA = 50. ,body = "Phobos", LKofT = "T", PFlux = "T", Lon_Hr = 8.)
...if standard flux values are acceptable (i.e., broad assumption on Mars surface temperature, and albedo). Fluxes are set with PFlux = "T", and by setting Lon_Hr.
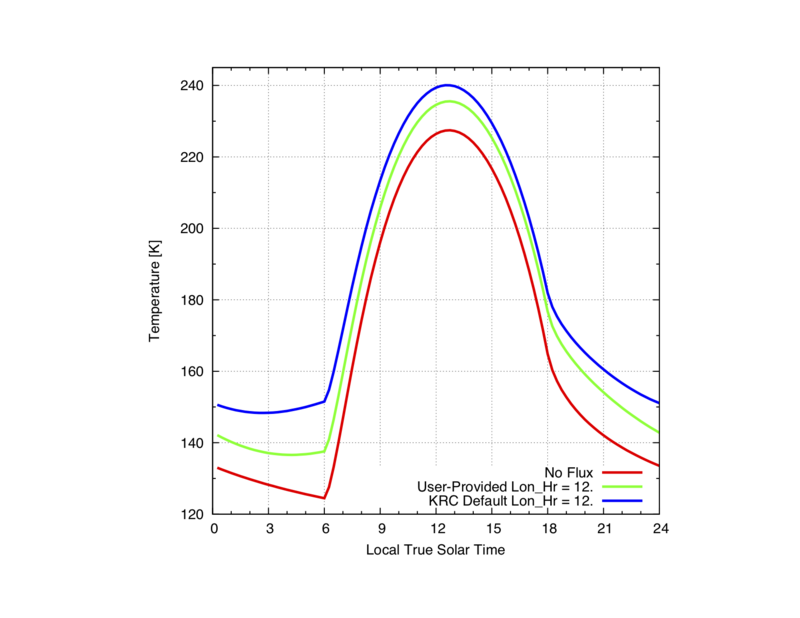
Lon_Hr is the surface longitude relative to the sub-Mars point, expressed in hours. Phobos being tidally locked, Lon_Hr = 12. is the sub-Mars point (max fluxes), and 0. for the center longitude of Phobos hidden face. Note 18 < Lon_Hr%24 < 6 corresponds to the Phobos hidden face, so no fluxes are contributed in these cases.
Generally, for tidally locked bodies, the sub-planet point (sub Mars point for Phobos is located ~ at longitude = 0), so that Lon_Hr can be derived from the longitude modeled on Phobos ore any tidally locked body:
Lon_Hr = (24/360 x (180 - longitude west))%24
Alternatively, the user can provide Visible and IR fluxes versus local time (krc_planetary_flux_table() generates the input parameters). An external model or a set of dedicated KRC runs can be used to determine the IR and Visible flux versus local time, as seen from Lon_Hr and the specified latitude. The figure below shows the externally provided values ("IR External Model", and "Vis External Model", the associated sin fits fed to KRC by the interface ("IR KRC Fit", and "Vis KRC Fit"), and the difference between the external forcing and the KRC forcing ("KRC - External Model").
Note that a user might want to consider reducing the average difference between the KRC Fit and the external model by fine tuning the fits.
In this case, the flux from Mars on Phobos can be formalized like this:
out = krc(lat = 12. ,INERTIA = 50. ,body = "Phobos", LKofT = "T", PFlux = "T",Lon_Hr = 8., IR = IR_1, Vis = Vis_1)
See below a comparison of the predicted surface temperature with and without Mars IR and visible shine on Phobos:
 Comparison between No Flux, and Flux at the Sub Mars point
Comparison between No Flux, and Flux at the Sub Mars point
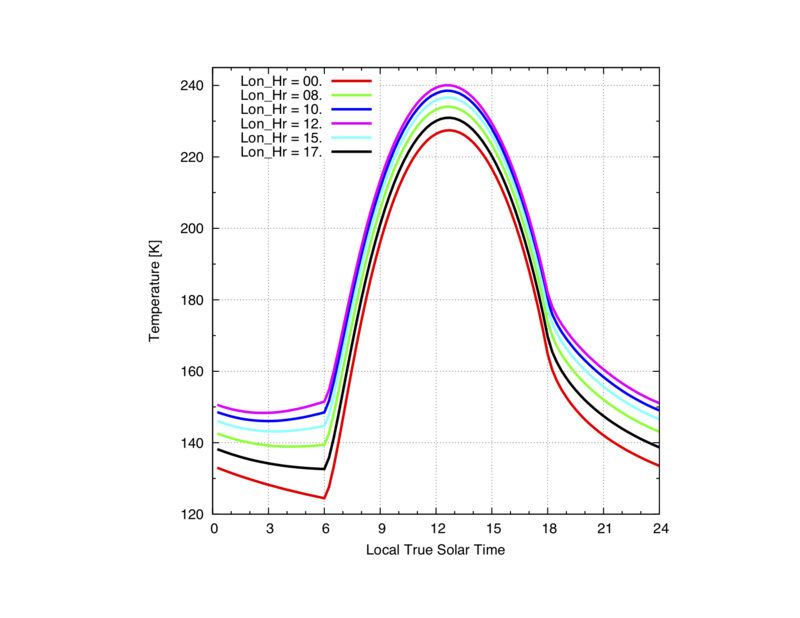 Comparison between No Flux, and Flux received from the hidden face (none), i.e., no forcing.
Comparison between No Flux, and Flux received from the hidden face (none), i.e., no forcing.