KRC for Europa
(→Eclipse by Jupiter) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Water ice is the default material for Europa (Mat1 = "H2O"), and T_user = 100 (temperature at which the inertia is defined). | ||
Some parameters are set to realistic values by default, including: | Some parameters are set to realistic values by default, including: | ||
| − | :Mat1 = "H2O" which | + | :Mat1 = "H2O" which assigns water ice Cp, Density, and Conductivity properties |
| − | :Mat2 = "H2O" which | + | :Mat2 = "H2O" which assigns water ice Cp, Density, and Conductivity properties |
:ALBEDO = 0.67 | :ALBEDO = 0.67 | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
When running the DaVinci interface, default Mars atmospheric values might be printed on the screen but not effectively used (PTOTAL = 0.) | When running the DaVinci interface, default Mars atmospheric values might be printed on the screen but not effectively used (PTOTAL = 0.) | ||
| − | == | + | == Simple Cases == |
Basic surface temperatures for Europa: | Basic surface temperatures for Europa: | ||
| − | + | OUT = krc(lat=0,INERTIA=45.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,LKofT="F") | |
| − | [[Image:Europa_F01.png| | + | [[Image:Europa_F01.png|800px]] Example of simple diurnal temperature curve |
labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]") | labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]") | ||
plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"45 Kieffer, No Flux",w=2,color=2) | plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"45 Kieffer, No Flux",w=2,color=2) | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | == Planetary Flux (From Jupiter) == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
::When Lon_Hr > 18, the surface point is on the Antijovian hemisphere => No flux contributed. | ::When Lon_Hr > 18, the surface point is on the Antijovian hemisphere => No flux contributed. | ||
| − | dv> OUT = krc(lat = 0., INERTIA = 70., body = " | + | dv> OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") |
''2: Provide values for all the necessary input parameters, and set PFlux = "T" (Default provided for common bodies)'' | ''2: Provide values for all the necessary input parameters, and set PFlux = "T" (Default provided for common bodies)'' | ||
| − | ::BT_Avg : Average Brightness Temperature [K] | + | ::'''BT_Avg''' : Average Brightness Temperature [K] |
| − | ::BT_Min : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K] | + | ::'''BT_Min''' : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K] |
| − | ::BT_Max : Max Brightness Temperature [K] | + | ::'''BT_Max''' : Max Brightness Temperature [K] |
| − | ::Dis_AU : Distance from Sun in AU | + | ::'''Dis_AU''' : Distance from Sun in AU |
| − | ::Geom_alb : Geometric Albedo [1] | + | ::'''Geom_alb''' : Geometric Albedo [1] |
| − | ::Mut_Period : Mutual Period [?] | + | ::'''Mut_Period''' : Mutual Period [?] |
| − | ::Orb_Radius : Orbiting Radius [km] | + | ::'''Orb_Radius''' : Orbiting Radius [km] |
| − | ::Radius : Radius of the Obiting body [km] | + | ::'''Radius''' : Radius of the Obiting body [km] |
| − | ::Lon_Hr : Longitude Hour of the surface point (see above) | + | ::'''Lon_Hr''' : Longitude Hour of the surface point (see above) |
| − | + | OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",BT_Avg=127.,BT_Min=127.,BT_Max=127.,Dis_AU=5.203,Geom_alb=0.52,Mut_Period=3.55,Orb_Radius=670900,Radius=670900,Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") | |
| Line 72: | Line 75: | ||
::Vis: A 2 x n x 1 array with Vis flux (1st col.) vs. LTST (2nd col.) | ::Vis: A 2 x n x 1 array with Vis flux (1st col.) vs. LTST (2nd col.) | ||
| − | dv> OUT = krc(lat = 0., INERTIA = 70., body = " | + | dv> OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") |
| − | [[Image:Europa_F02.png| | + | [[Image:Europa_F02.png|800px]] Comparison between simple diurnal temperature curves (with vs. without Jupiter flux) |
| − | + | OUT_2 = krc(lat=0,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55, LKofT="F") | |
| − | + | OUT_3 = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F") | |
| − | + | labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]") | |
| − | + | plot(OUT_2.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT_2.time,"70 Kieffer, No Flux",w=2,color=2,OUT_3.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT_3.time,"70 Kieffer,With Flux",w=2,color=3) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Eclipse by Jupiter == | ||
| Line 87: | Line 92: | ||
:Eclipse = "T" forces an eclipse (Default = "F") | :Eclipse = "T" forces an eclipse (Default = "F") | ||
| − | :body = " | + | :body = "Europa" |
| − | :Eclipser = " | + | :Eclipser = "Jupiter" Eclipser name, for Example "Jupiter" or "Mars" |
:Eclipse_Style = 1 because eclipses are assumed to occur daily; see dedicated Eclipse Section [Build Link Here] | :Eclipse_Style = 1 because eclipses are assumed to occur daily; see dedicated Eclipse Section [Build Link Here] | ||
| Line 99: | Line 104: | ||
:Date: ??? | :Date: ??? | ||
| − | + | OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=45.,N1=32,body="Europa",N24=96,Eclipse="T",Eclipser="Jupiter",Ecl_Cent_Hr=12.,Bias=0.,Eclipse_Style=1.,Date=5000.) | |
| − | [[Image:Europa_F03.png| | + | [[Image:Europa_F03.png|800px]] Example of Europa diurnal curve with Jupiter Eclipse centered at Noon |
labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]","45 Kieffer, Eclipse centered at Noon") | labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]","45 Kieffer, Eclipse centered at Noon") | ||
| − | plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"Noon Eclipse") | + | plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"Noon Eclipse") |
| − | + | ||
| + | == Defining a Date == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Seasons can be defined as Ls (ls), Julian Date (JD), and Gregorian Date (GD): | ||
| + | |||
| + | OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=25.,ls=90.) | ||
| + | For a specific Gregorian Date, GD (currently ranging from 1990-Jan-01 to 2040-Jan-01), the format is ????-Mmm-DD, | ||
| + | with Mmm:Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec; | ||
| − | == | + | OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=12.,GD="2010-Jan-05") |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | or a specific Julian Date JD: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=12.,JD=2455201) |
| − | + | Note: the possibility to specify the date with GD is only currently available for Mars, the Moon, Bennu, and Europa. | |
Latest revision as of 16:24, 14 May 2020
Contents |
[edit] Notes
Water ice is the default material for Europa (Mat1 = "H2O"), and T_user = 100 (temperature at which the inertia is defined).
Some parameters are set to realistic values by default, including:
- Mat1 = "H2O" which assigns water ice Cp, Density, and Conductivity properties
- Mat2 = "H2O" which assigns water ice Cp, Density, and Conductivity properties
- ALBEDO = 0.67
- PTOTAL = 0 which eliminates the atmosphere (ELEV, TAU, etc. unused)
When running the DaVinci interface, default Mars atmospheric values might be printed on the screen but not effectively used (PTOTAL = 0.)
[edit] Simple Cases
Basic surface temperatures for Europa:
OUT = krc(lat=0,INERTIA=45.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,LKofT="F")
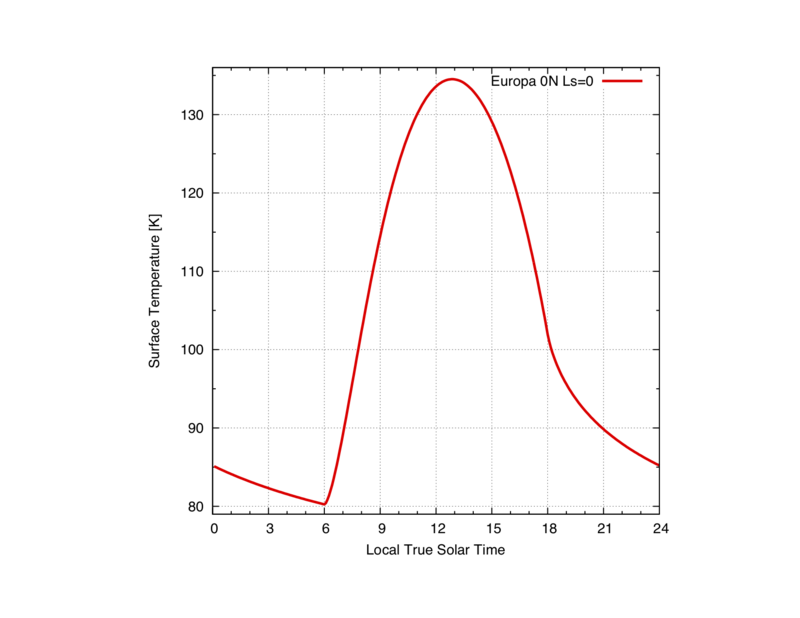 Example of simple diurnal temperature curve
Example of simple diurnal temperature curve
labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]")
plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"45 Kieffer, No Flux",w=2,color=2)
[edit] Planetary Flux (From Jupiter)
To include the visible and thermal infrared flux from Jupiter, three approaches are possible:
1: Use default built-in parameters, set PFlux = "T", and Lon_Hr
- Lon_Hr [0-24] is the surface longitude relative to the sub-Jupiter point, expressed in hours.
- When Lon_Hr < 6, the surface point is on the Antijovian hemisphere => No flux contributed.
- When 6 < Lon_Hr < 18, the surface point is on the subjoin hemisphere => Flux is contributed (max at Lon_Hr = 12.).
- When Lon_Hr > 18, the surface point is on the Antijovian hemisphere => No flux contributed.
dv> OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
2: Provide values for all the necessary input parameters, and set PFlux = "T" (Default provided for common bodies)
- BT_Avg : Average Brightness Temperature [K]
- BT_Min : Min Brightness Temperature, if diurnal cycle [K]
- BT_Max : Max Brightness Temperature [K]
- Dis_AU : Distance from Sun in AU
- Geom_alb : Geometric Albedo [1]
- Mut_Period : Mutual Period [?]
- Orb_Radius : Orbiting Radius [km]
- Radius : Radius of the Obiting body [km]
- Lon_Hr : Longitude Hour of the surface point (see above)
OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",BT_Avg=127.,BT_Min=127.,BT_Max=127.,Dis_AU=5.203,Geom_alb=0.52,Mut_Period=3.55,Orb_Radius=670900,Radius=670900,Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
3: Provide Visible and IR flux tables vs. LTST, and set PFlux = "T"
- The interface fits sin functions through the table values, and extracts parameters required by KRC (amplitude, phase, etc.). For Europa, this is not the preferred option.
- IR: A 2 x n x 1 array with IR flux (1st col.) vs. LTST (2nd col.)
- Vis: A 2 x n x 1 array with Vis flux (1st col.) vs. LTST (2nd col.)
dv> OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
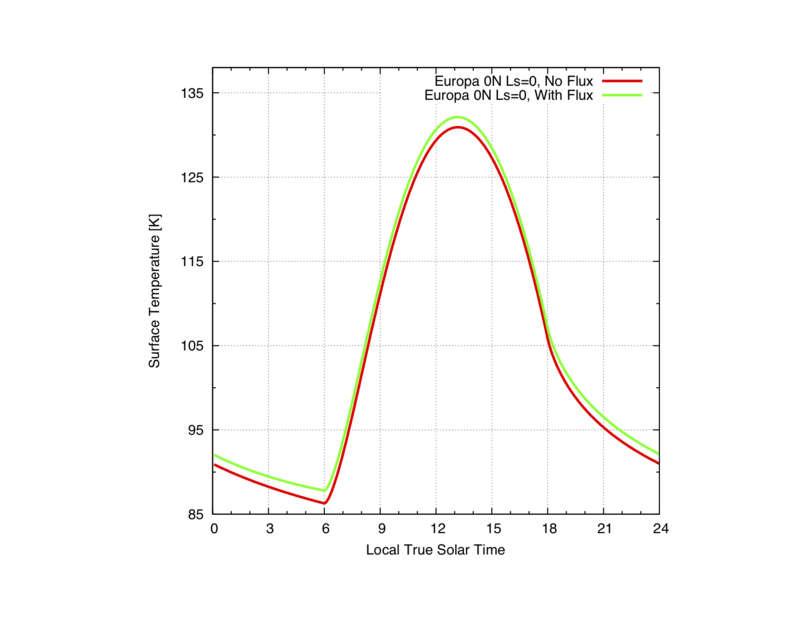 Comparison between simple diurnal temperature curves (with vs. without Jupiter flux)
Comparison between simple diurnal temperature curves (with vs. without Jupiter flux)
OUT_2 = krc(lat=0,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55, LKofT="F")
OUT_3 = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=70.,body="Europa",ALBEDO=.55,PFlux="T",Lon_Hr=12.,LKofT="F")
labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]")
plot(OUT_2.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT_2.time,"70 Kieffer, No Flux",w=2,color=2,OUT_3.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT_3.time,"70 Kieffer,With Flux",w=2,color=3)
[edit] Eclipse by Jupiter
To include an Eclipse by Jupiter, set Eclipse = "T" and specify the following parameters:
- Eclipse = "T" forces an eclipse (Default = "F")
- body = "Europa"
- Eclipser = "Jupiter" Eclipser name, for Example "Jupiter" or "Mars"
- Eclipse_Style = 1 because eclipses are assumed to occur daily; see dedicated Eclipse Section [Build Link Here]
- Ecl_Cent_Hr: Eclipse central hour [subjovian point => =12.; Antijovian point => =0.]
- Bias = 0.0: Eclipse Bias (0 => perfect alignement; 1 => partial eclipse); see dedicated Eclipse Section [Build Link Here]
- Date: ???
OUT = krc(lat=0.,INERTIA=45.,N1=32,body="Europa",N24=96,Eclipse="T",Eclipser="Jupiter",Ecl_Cent_Hr=12.,Bias=0.,Eclipse_Style=1.,Date=5000.)
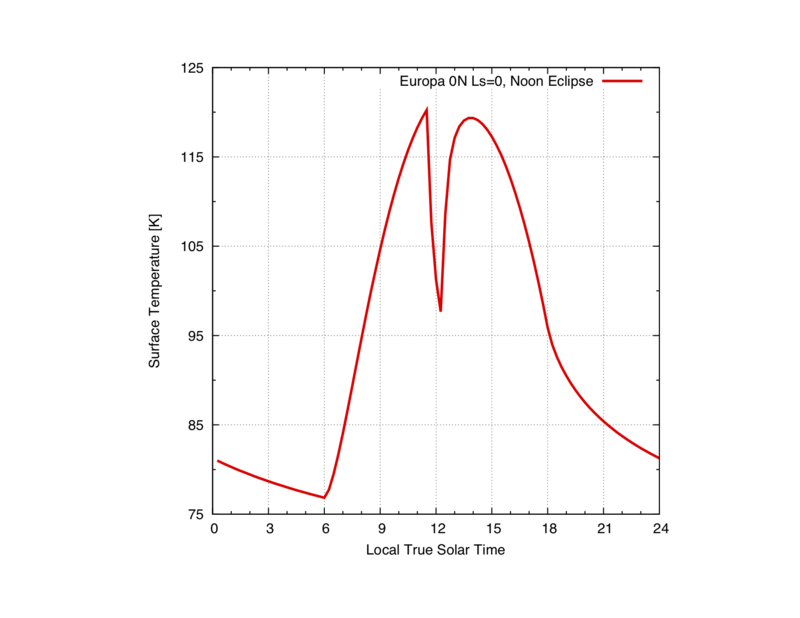 Example of Europa diurnal curve with Jupiter Eclipse centered at Noon
Example of Europa diurnal curve with Jupiter Eclipse centered at Noon
labelxy("LTST","Temperature [K]","45 Kieffer, Eclipse centered at Noon")
plot(OUT.tsurf[,1,1],xaxis=OUT.time,"Noon Eclipse")
[edit] Defining a Date
Seasons can be defined as Ls (ls), Julian Date (JD), and Gregorian Date (GD):
OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=25.,ls=90.)
For a specific Gregorian Date, GD (currently ranging from 1990-Jan-01 to 2040-Jan-01), the format is ????-Mmm-DD, with Mmm:Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec;
OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=12.,GD="2010-Jan-05")
or a specific Julian Date JD:
OUT = krc(body="Europa",lat=12.,JD=2455201)
Note: the possibility to specify the date with GD is only currently available for Mars, the Moon, Bennu, and Europa.